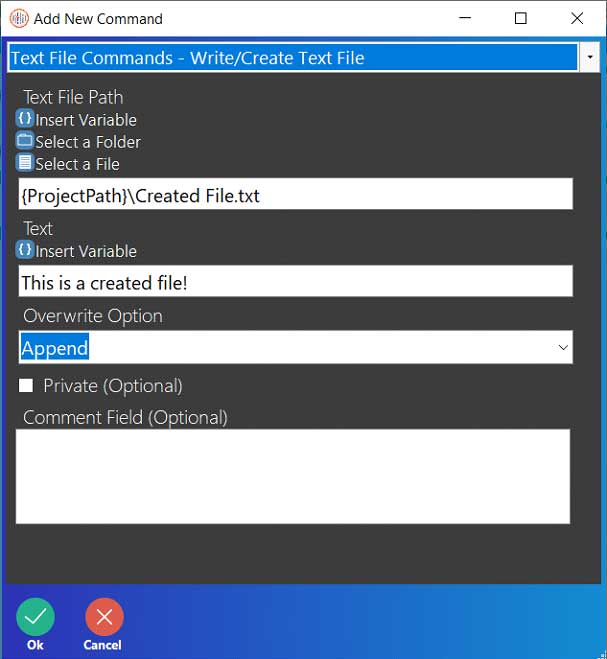
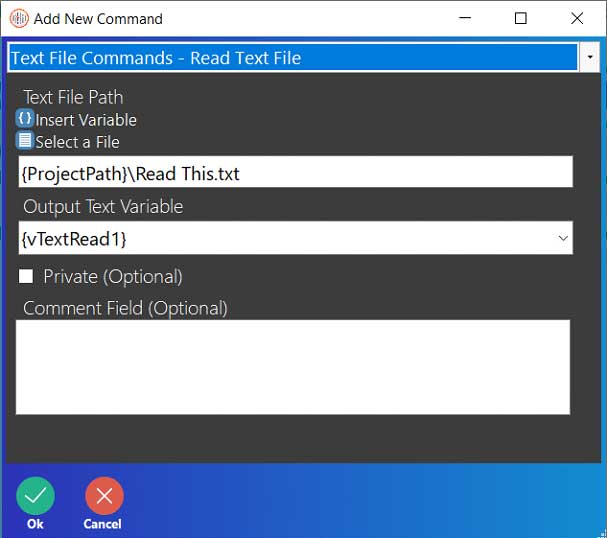
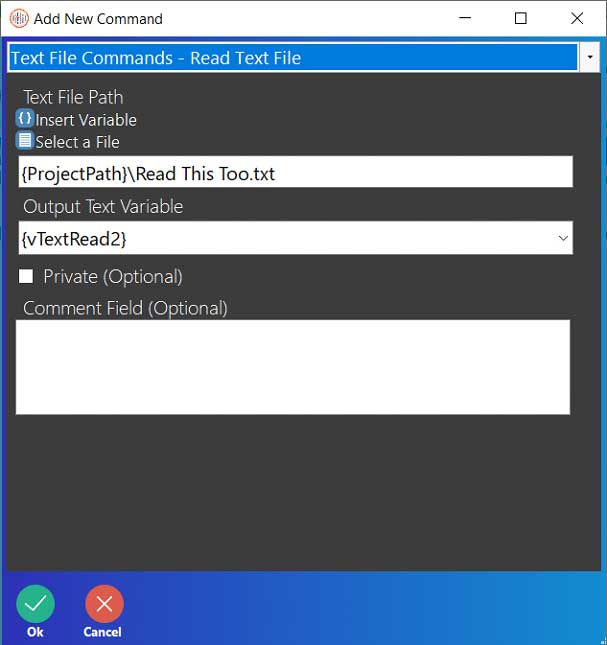
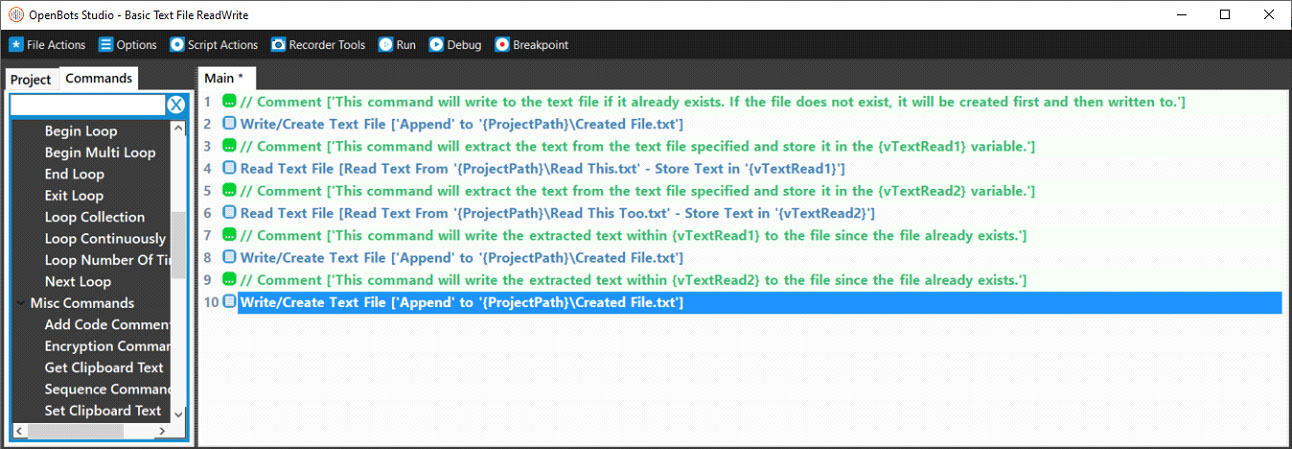
Step 1: Text files, unlike Excel commands, do not need an instance name simply because text files are simple documents that can, unsurprisingly, only store text. This means that there aren’t very many commands for text files to use. The first Text File command that will be used is the Write/Create Text File command. This command can be used to either write to an existing file or create and then write to a new text file.
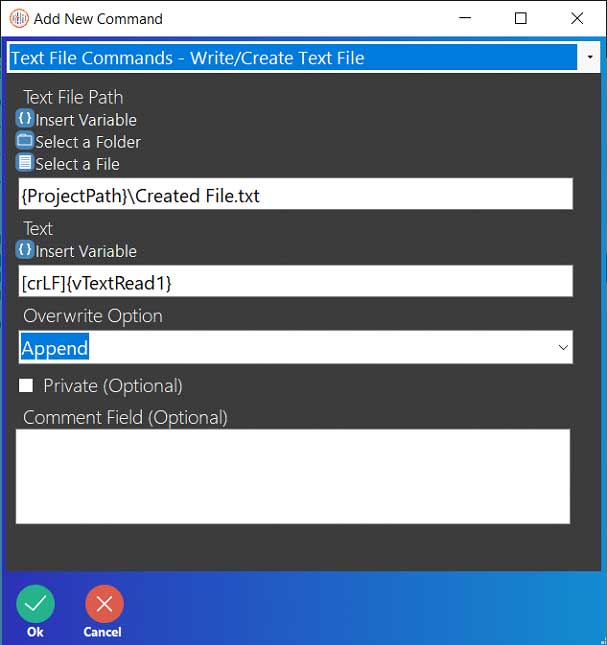
- Select the Write/Create Text File command.
- Enter the file path for a text file. (If the file specified in the Text File Path does not exist, then this command will create it with the name specified in the field itself. If it does already exist, then it will simply write to the file. In this guide, the file specified file does not exist and will be created by this command.)
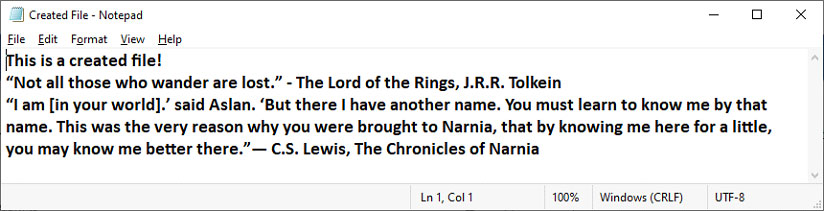
- In the Text field, write a message that indicates that this file was just created.
- In the Overwrite Option field, choose either “Append” or “Overwrite”. At this point, it does not matter which option is chosen. (The difference between the options is that “Append” will add the specified text to the end of the last line in the text file. This will NOT create a new line. The “Overwrite” option deletes everything in the file and writes the specified text on the first line.)
- Click OK.